Interleukins are associated primarily with which of the following? This question delves into the fascinating world of interleukins, a group of cytokines that play a crucial role in various immune responses, cell growth, and differentiation. Their intricate functions and involvement in both health and disease make them a topic of significant interest in the field of immunology.
Interleukins are produced by a diverse range of immune cells and stromal cells, and their production is tightly regulated to ensure appropriate immune responses. They exert their effects by binding to specific receptors on target cells, triggering intracellular signaling cascades that lead to various cellular responses.
Interleukin Functions
Interleukins are a group of cytokines that play a crucial role in immune responses, cell growth, and differentiation. They are produced by various cell types, including immune cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts. Interleukins regulate a wide range of biological processes, including:
- Immune responses:Interleukins are involved in the activation, proliferation, and differentiation of immune cells. They regulate the production of antibodies, cytokines, and other immune mediators, facilitating the immune response against pathogens.
- Cell growth and differentiation:Interleukins promote the growth, proliferation, and differentiation of various cell types. They play a crucial role in hematopoiesis, the development of blood cells, and the regulation of cell cycle progression.
- Inflammation:Interleukins are key mediators of inflammation. They regulate the recruitment and activation of immune cells to sites of infection or injury, promoting the inflammatory response and tissue repair.
- Hematopoiesis:Interleukins are essential for the production and differentiation of blood cells. They regulate the growth and development of stem cells, as well as the maturation of various types of blood cells.
- Bone metabolism:Interleukins are involved in bone remodeling and metabolism. They regulate the differentiation and activation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, cells responsible for bone formation and resorption, respectively.
Interleukin Production and Regulation
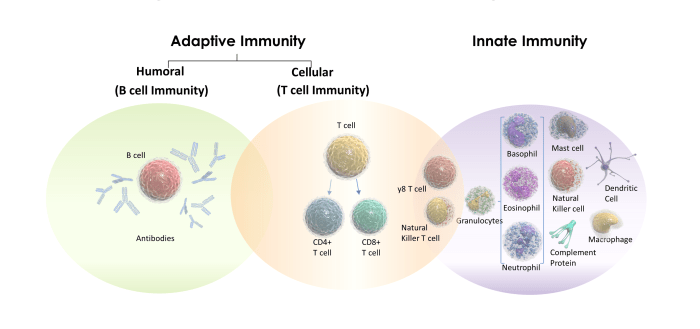
The production of interleukins is tightly regulated to ensure appropriate immune responses and cellular functions. Interleukins are primarily produced by immune cells, such as macrophages, T cells, and B cells, in response to various stimuli, including:
- Pathogens:Infection by bacteria, viruses, or parasites triggers the production of interleukins by immune cells, initiating an immune response.
- Cytokines:Other cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), can stimulate the production of interleukins, amplifying the immune response.
- Antigens:The presence of foreign antigens, such as those on the surface of pathogens, can induce the production of interleukins by antigen-presenting cells.
- Cell damage:Damage to cells, such as that caused by trauma or inflammation, can release intracellular molecules that trigger the production of interleukins.
The regulation of interleukin production involves several mechanisms, including:
- Feedback loops:Interleukins themselves can regulate their own production through feedback loops. For example, IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1 and IL-6.
- Soluble receptors:Soluble receptors for interleukins can bind to the cytokines and prevent them from interacting with their cell surface receptors, thereby inhibiting their signaling.
- Intracellular inhibitors:Cells can produce intracellular inhibitors that block the signaling pathways activated by interleukins.
Interleukin Receptors and Signaling Pathways
Interleukins exert their biological effects by binding to specific receptors on the surface of target cells. These receptors belong to the cytokine receptor superfamily and are characterized by an extracellular domain that binds to the interleukin and an intracellular domain that initiates signaling pathways.Upon
interleukin binding, the receptor undergoes a conformational change that triggers the recruitment of intracellular signaling molecules. These molecules, such as Janus kinases (JAKs) and signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs), become phosphorylated and activate downstream signaling pathways.The signaling pathways activated by interleukins include:
- JAK/STAT pathway:This pathway is activated by many interleukins, including IL-2, IL-4, and IL-6. JAKs phosphorylate STATs, which then dimerize and translocate to the nucleus, where they regulate gene transcription.
- MAPK pathway:The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is activated by some interleukins, such as IL-1 and IL-17. MAPKs regulate cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
- NF-κB pathway:The nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) pathway is activated by pro-inflammatory interleukins, such as IL-1 and IL-6. NF-κB regulates the transcription of genes involved in inflammation, immunity, and cell survival.
Helpful Answers: Interleukins Are Associated Primarily With Which Of The Following
What are the primary functions of interleukins?
Interleukins are involved in a wide range of functions, including regulating immune responses, promoting cell growth and differentiation, and mediating inflammatory processes.
How are interleukins produced and regulated?
Interleukins are produced by various immune cells and stromal cells. Their production is tightly regulated by a complex network of cytokines, growth factors, and signaling molecules.
What are the different types of interleukin receptors?
Interleukins bind to specific receptors on target cells, triggering intracellular signaling cascades. There are various types of interleukin receptors, each with its unique signaling pathway.