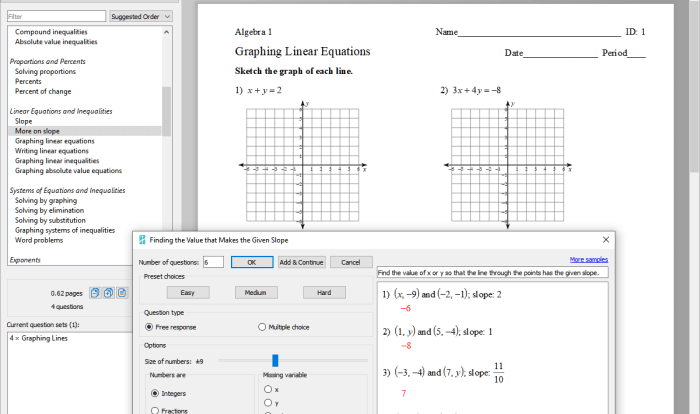
Introducing the Quadratic Functions and Equations Unit Test Part 1, an exploration into the captivating world of quadratic functions and equations. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental concepts, methods, and applications of these mathematical tools, equipping you with a solid understanding and practical skills.
Throughout this unit, we will uncover the defining characteristics of quadratic functions, delve into the techniques for solving quadratic equations, master the art of graphing these functions, and explore their versatile applications in real-world scenarios. Prepare to embark on an engaging and enlightening journey into the realm of quadratic functions and equations.
Quadratic Functions and Equations
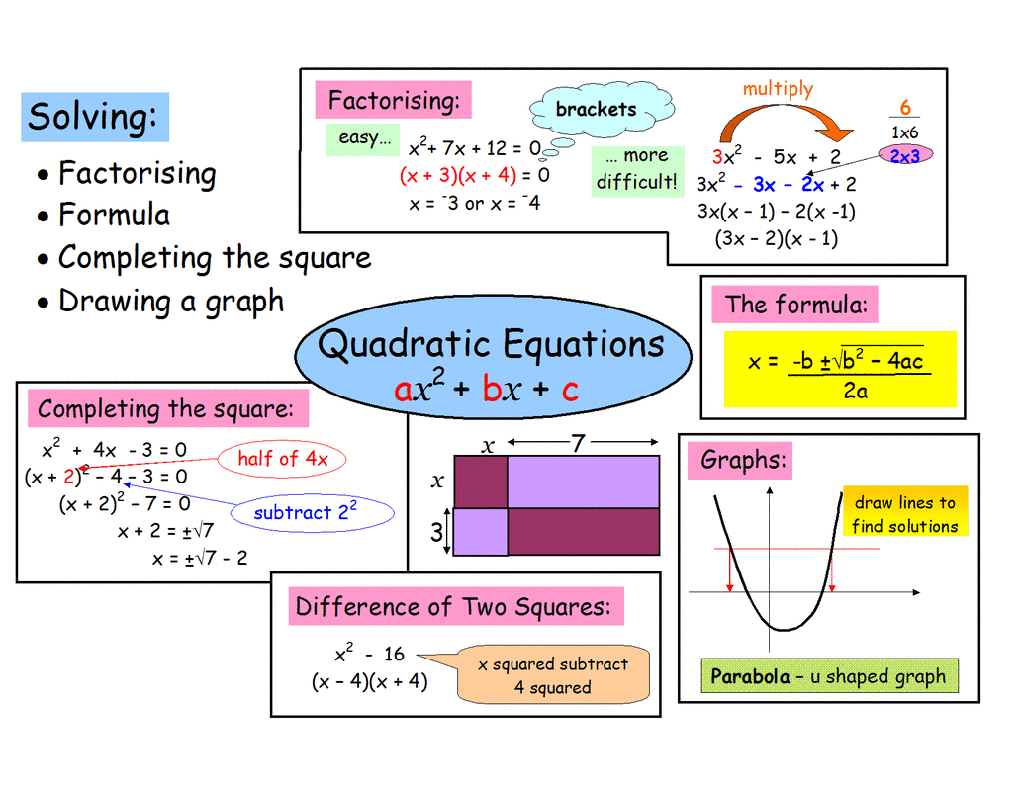
Quadratic functions are a class of mathematical functions that are widely used to model real-world phenomena. They are defined by their characteristic parabolic shape and have applications in various fields such as physics, engineering, and economics.
Quadratic Functions: Quadratic Functions And Equations Unit Test Part 1

A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree 2, represented in the standard form as:
$$f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c$$
where a, b, and care real numbers, and ais non-zero.
Components of a Quadratic Function
- a: The coefficient of the squared term, which determines the overall shape of the parabola.
- b: The coefficient of the linear term, which affects the horizontal translation of the parabola.
- c: The constant term, which determines the vertical translation of the parabola.
Vertex of a Parabola
The vertex of a parabola is the point where it changes direction. It is given by the coordinates:
$$(h, k) = \left(-\fracb2a, f\left(-\fracb2a\right)\right)$$
The vertex is a significant point as it represents the minimum or maximum value of the quadratic function.
Solving Quadratic Equations
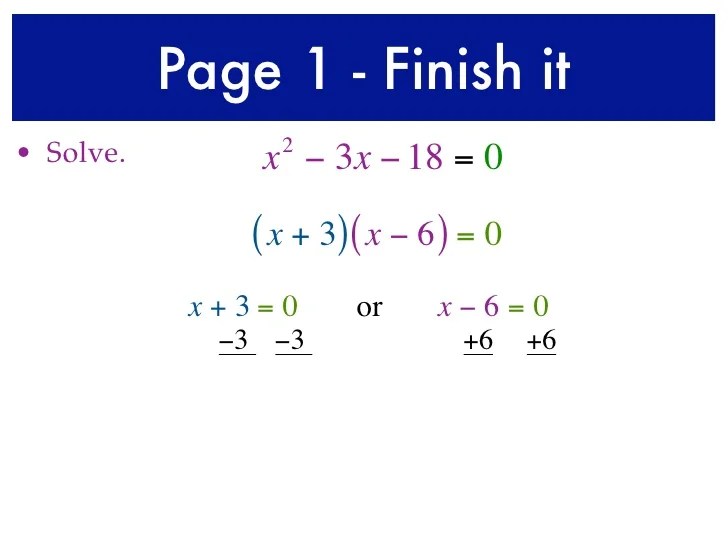
There are several methods to solve quadratic equations, including:
- Factoring
- Completing the square
- Quadratic formula
Discriminant
The discriminant is a term that determines the nature of the solutions to a quadratic equation. It is given by the expression:
$$D = b^2
4ac$$
The discriminant can have three possible values:
- D> 0: Two distinct real solutions
- D= 0: One real solution (a double root)
- D< 0: No real solutions (complex conjugate solutions)
Graphing Quadratic Functions
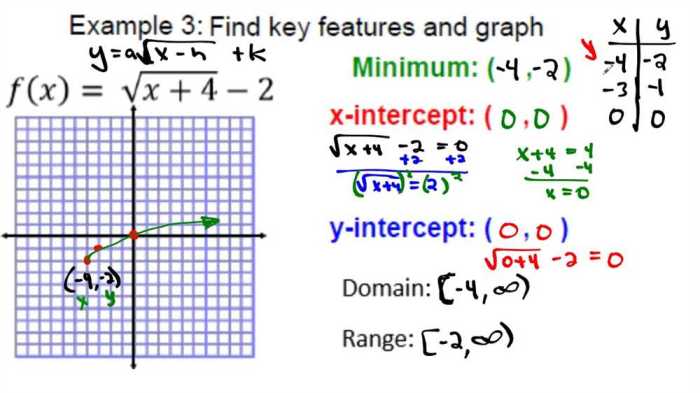
Quadratic functions can be graphed using the following steps:
- Find the vertex.
- Plot the vertex.
- Find the intercepts (x-intercepts and y-intercept).
- Plot the intercepts.
- Draw a smooth curve through the vertex and intercepts to form the parabola.
Effects of Changing Coefficients, Quadratic functions and equations unit test part 1
Changing the coefficients of a quadratic function affects the shape and position of its graph:
- a: Changes the overall shape of the parabola (wider or narrower).
- b: Shifts the parabola horizontally.
- c: Shifts the parabola vertically.
Applications of Quadratic Functions
Quadratic functions have numerous applications in real-world scenarios:
- Projectile motion
- Area of a parabola
- Optimization problems
Limitations
While quadratic functions are useful for modeling certain phenomena, it is important to note their limitations:
- They assume a parabolic shape, which may not always be accurate in real-world scenarios.
- They do not account for external factors that may influence the outcome.
Popular Questions
What is the standard form of a quadratic function?
The standard form of a quadratic function is ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a is not equal to 0.
How can I solve a quadratic equation using the quadratic formula?
The quadratic formula is x = (-b ± √(b^2 – 4ac)) / 2a. Plug in the values of a, b, and c from your equation and simplify to find the solutions.
What is the significance of the discriminant in a quadratic equation?
The discriminant, b^2 – 4ac, determines the nature of the solutions to a quadratic equation. If the discriminant is positive, there are two real solutions. If the discriminant is zero, there is one real solution (a double root). If the discriminant is negative, there are no real solutions (two complex solutions).